Dupuytren’s disease, also called palmar fibromatosis, is a condition that slowly affects the hand. It begins with thickening of the connective tissue in the palm, which forms nodules.
Over time, the condition progresses and leads to finger contracture. This means the fingers, usually the ring and little fingers, start bending toward the palm and cannot straighten completely.
This disease is often referred to as Viking disease due to its high prevalence in people of Northern European ancestry.
Common Causes of Dupuytren’s Disease
The exact cause of Dupuytren’s disease is not fully understood, but genetics play a major role. It commonly runs in families, making it a hereditary condition. Men over 50 years of age are more likely to develop it.
People with Northern European backgrounds also have a higher chance of being affected. Lifestyle choices like smoking and alcohol consumption may increase the risk.
Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes, epilepsy, and liver disease are also linked to the condition. These factors contribute to the abnormal buildup of collagen, leading to thickened fascia and the formation of fascial bands in the palm.
Understanding the Causes Behind Loguytren Problems
Loguytren problems, or Dupuytren’s disease, are mainly caused by genetics and are more common in men over 40, especially those of Northern European ancestry.
Other risk factors include diabetes, smoking, alcohol use, and certain health conditions like epilepsy and liver disease. The condition causes the tissue in the palm to thicken, leading to bent fingers over time.
Symptoms of Dupuytren’s Disease
The early signs include small, hard lumps or nodules under the skin of the palm. These nodules may feel tender at first, but the discomfort usually fades. As the disease progresses, these lumps form thick cords under the skin.
The skin on the palm may appear dimpled or puckered. Eventually, one or more fingers begin to bend inward and cannot be straightened. The condition mainly affects the ring and little fingers.
Over time, hand function becomes limited, and tasks like grasping objects or shaking hands become difficult.
What Exactly Are Loguytren Problems?
Loguytren problems likely refer to Dupuytren’s disease a medical condition that affects the connective tissue in the palm of the hand, causing finger contractures.
Over time, thickened tissue under the skin forms nodules or cords, which can pull one or more fingers (often the ring or little finger) into a bent position. These fingers may become difficult or impossible to straighten, leading to reduced hand function.
This condition is also known as Dupuytren’s contracture, palmar fibrosis, or colloquially, Viking disease, due to its high incidence in people of Northern European ancestry. It is a progressive connective tissue disorder and typically develops slowly over many years.
How Dupuytren’s Disease Affects Daily Life?
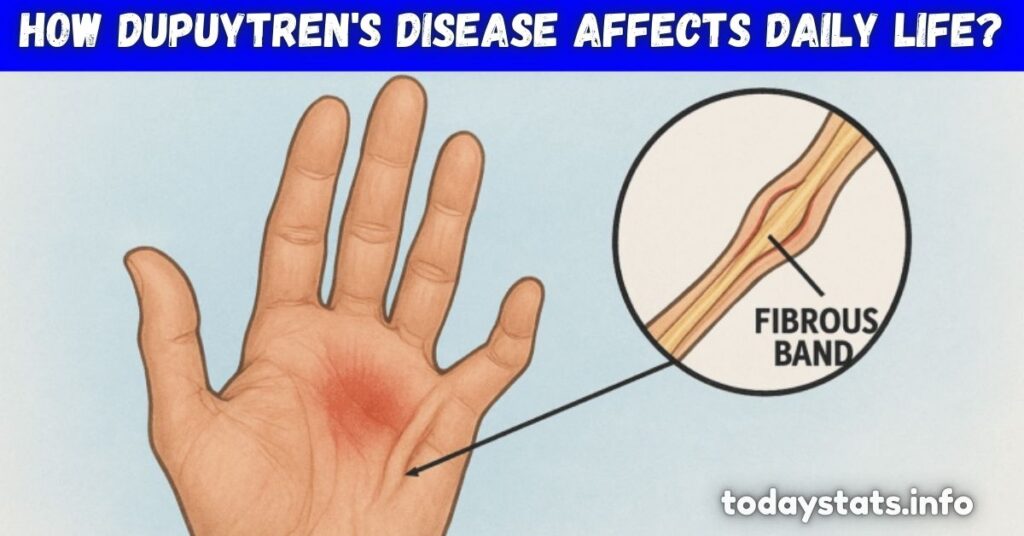
As finger contracture worsens, normal hand movement becomes restricted. People may struggle with basic activities such as holding utensils, typing, writing, or buttoning clothes.
Personal hygiene tasks, like washing hands or brushing teeth, may become challenging. In severe cases, people may find it difficult to perform their jobs, especially if their work involves fine motor skills.
This limited hand function can impact independence and reduce quality of life. Emotional frustration and stress are also common due to the condition’s progressive nature.
Treatment Options for Dupuytren’s Disease
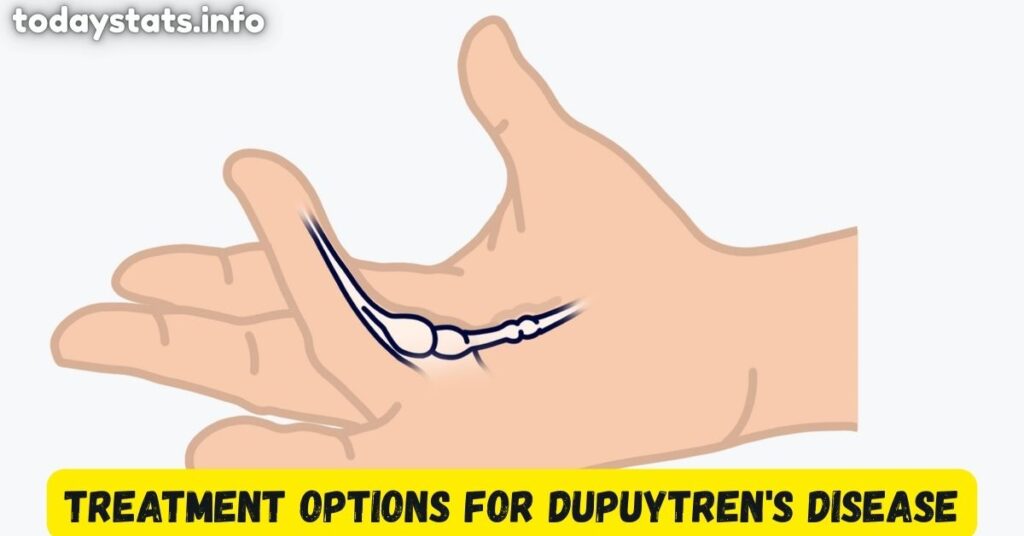
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the disease. In mild cases, no treatment may be necessary, and doctors may suggest observation and regular monitoring.
If the contracture starts to interfere with daily tasks, several options are available. Collagenase injections are a non-surgical treatment where enzymes are injected into the cord to break it down.
Needle aponeurotomy is another non-invasive technique that uses a fine needle to release the cord. Surgery is often recommended for more advanced cases. Fasciectomy involves removing the thickened tissue.
Dermofasciectomy may be needed for severe or recurring cases. After any procedure, hand therapy helps restore strength and flexibility. Treatment is tailored to the individual depending on the severity and lifestyle needs.
Preventing Dupuytren’s Disease
Since Dupuytren’s disease is largely hereditary, prevention can be challenging. However, certain actions may help delay the onset or reduce severity. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake may reduce the risk.
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes can also play a role in prevention. Regular hand exercises may help maintain flexibility and strength in the fingers. People with a family history should pay attention to early signs such as palm thickening or the formation of nodules.
Early detection allows for timely medical evaluation and may improve long-term outcomes. Being proactive in managing risk factors can support better hand health.
When to See a Doctor About Dupuytren’s Disease?
Medical advice should be sought if you notice persistent lumps in your palm. If your fingers are beginning to bend and you find it difficult to straighten them, it’s important to get checked.
Interference with everyday tasks such as gripping, writing, or grooming may indicate that the disease is progressing. Early diagnosis and treatment can slow the progression and help maintain hand function.
A specialist will examine your hand and may suggest imaging or functional tests. Timely consultation is important to explore all possible treatment options before the condition becomes disabling.
READ THIS BLOG: Glow Up Routine: The Ultimate Guide to soinducorpsetdesmains
Living with Dupuytren’s Disease
Managing Dupuytren’s disease is a long-term process. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider help monitor disease progression. Hand therapy can improve mobility and maintain strength.
Patients may also benefit from using assistive tools to make daily tasks easier. Support groups and education about the disease can provide encouragement and helpful tips. Emotional well-being is just as important as physical health, so seeking support when needed is essential.
Staying informed and involved in your care plan helps you adapt to changes and maintain independence. With proper management, people can continue to lead active lives despite the condition.
Living with Loguytren Problems: Managing the Daily Impact
Living with Loguytren problems means adjusting to changes in hand function caused by finger contracture. As the condition progresses, it becomes harder to do everyday tasks like writing, buttoning clothes, holding tools, or even shaking hands.
Simple routines such as grooming, cooking, or using a phone can become frustrating.To manage the impact, many people rely on hand therapy to maintain flexibility and slow down stiffness.
Using adaptive tools like utensils with larger grips or voice-to-text apps can make daily life easier. In some cases, treatment like injections or surgery may improve mobility and reduce limitations.
Staying active, doing regular hand exercises, and having regular check-ups can help manage the condition. Emotional support and patience are important too, especially when dealing with the gradual loss of hand strength or dexterity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Dupuytren’s disease?
Dupuytren’s disease is a condition where the connective tissue in the palm becomes thick and forms cords that cause finger contracture.
Who is most at risk for Dupuytren’s disease?
People with a family history, men over 50, and individuals of Northern European ancestry are at higher risk.
Is Dupuytren’s disease painful?
In most cases, it is not painful, but some people may feel tenderness or discomfort in the palm.
Can Dupuytren’s disease be cured?
There is no cure, but treatments like enzyme injections and surgery can reduce symptoms and improve hand function.
Does Dupuytren’s disease come back after treatment?
Yes, the condition can recur even after successful treatment, so ongoing monitoring is necessary.
Conclusion
Dupuytren’s disease is a progressive connective tissue disorder that affects hand function and everyday activities. While the exact cause is not fully known, genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to its development.
Early detection is key to managing symptoms and slowing progression. There are several effective treatment options, including non-invasive and surgical approaches. Hand therapy plays an important role in recovery and maintaining movement.
Although there is no cure, people can live full, active lives with the right care and support. Being aware of symptoms and seeking timely medical advice ensures the best possible outcomes.

Smith is a seasoned SEO expert with a passion for content writing, keyword research, and web development. He combines technical expertise with creative strategies to deliver exceptional digital solutions.






